Create a budget in 6 steps
Developing a well-structured personal budget is pivotal for effective financial management. This process involves a detailed examination of all income streams, a thorough categorization of fixed and variable expenditures, the establishment of savings targets, and the formulation of strategies for debt repayment. By adopting a holistic approach, you ensure a comprehensive oversight of your financial landscape, leaving no stone unturned.
1. Cataloging Monthly Expenditures
Embarking on the path to financial prudence begins with an exhaustive inventory of your monthly outlays. This encompasses all aspects of your financial life, from significant obligations such as housing costs (rent or mortgage payments) to more discretionary spending like your daily café visits. Gaining insight into your expenditure patterns is the foundational step toward achieving financial mastery.
2. Assessing the Average Monthly Outlay for Each Expenditure in your personal budget
To refine your budgetary framework, it’s imperative to ascertain the average monthly cost associated with each of your expenses. This analytical approach provides a more nuanced understanding of your spending habits, facilitating the identification of potential areas for financial optimization.
3. Differentiating Between Fixed and Variable Expenses
A critical aspect of budgeting is the ability to differentiate between fixed and variable expenses. Fixed expenses, such as loan repayments or housing costs, are immutable month-to-month. In contrast, variable expenses, such as leisure activities or dining out, are more fluid and subject to change. Recognizing these distinctions is key to adapting your budget to enhance savings.
4. Implementing a Personal Budgeting Strategy
Grasping the intricacies of the budgeting process is about more than just tracking expenses; it’s about understanding the dynamics of your cash flow, pinpointing opportunities for cost reduction, and setting attainable financial objectives. Effective budgeting transforms your approach to money management, ensuring that your financial resources are allocated in a way that serves your long-term aspirations.
5. Selecting an Appropriate Personal Budgeting Method to create a budget
The realm of a personal budget is diverse, offering a variety of methodologies suited to different financial circumstances and preferences. From the zero-based budget, where every dollar is allocated a specific purpose, to the 50/30/20 rule, which provides a balanced approach to managing essentials, savings, and personal spending, and the envelope system, which uses physical cash allocations to curb overspending, there’s a strategy to suit every financial need. Choosing the right approach is essential for fostering a sustainable and effective budgeting practice.
Incorporating a budget into your financial planning is a dynamic process that can significantly influence your financial well-being. By establishing a personal budget, you gain clarity on your income versus expenditure, enabling you to make informed decisions that align with your long-term financial goals.
This clarity is instrumental in managing your money effectively, ensuring that you are well-prepared for both planned and unforeseen financial demands.
A well-crafted budget serves as a roadmap for your financial journey, guiding you through the complexities of income management, expense tracking, and savings accumulation. By dedicating time to understand and implement these budgeting steps, you position yourself to achieve financial stability, meet your savings objectives, and secure a prosperous future.
The 50/30/20 Rule.
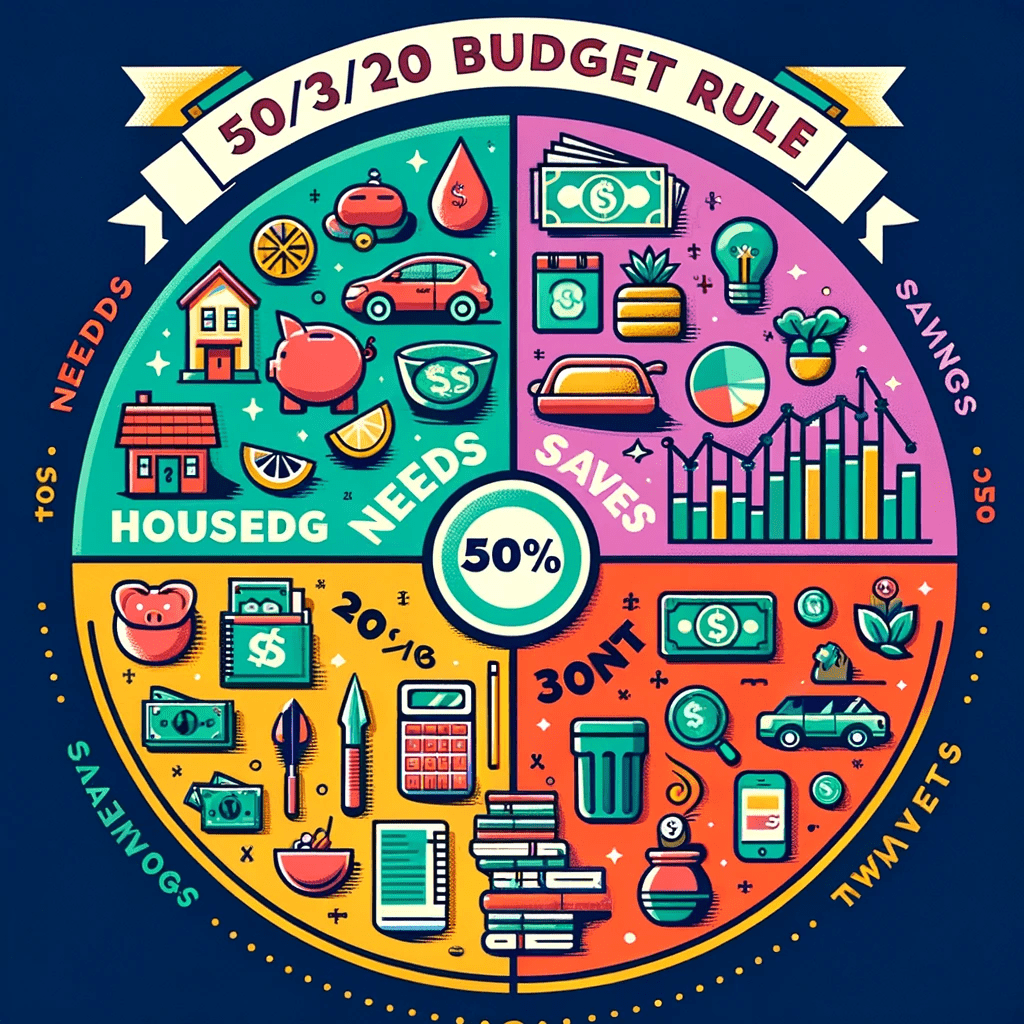
What is the 50 20 30 personal budget rule?
The 50-30-20 rule recommends putting 50% of your money toward needs, 30% toward wants, and 20% toward savings. The savings category also includes money you will need to realize your future goals
50% Allocation to Needs
At the heart of this budgeting plan is the principle that 50% of your net income should be allocated towards meeting your essential needs. These are expenditures that are fundamental to your daily living and well-being.
This segment of your budget encompasses housing costs such as rent or mortgage payments, utility bills, groceries, transportation expenses, healthcare, and other non-negotiable bills.
The critical challenge here is discerning between absolute necessities and expenses that, upon closer examination, can be adjusted or even eliminated. This discernment is crucial in maintaining the integrity of your budget and ensuring that your spending aligns with your essential needs.
20% Allocation to Savings and debt repayment
The 20% savings rule underscores the importance of prioritizing your financial future. This segment of your income is dedicated to building a robust financial foundation through savings and debt repayment. Contributions to an emergency fund, retirement savings accounts, investment portfolios, and the reduction of high-interest debt such as credit card balances and loans fall under this category.
The emphasis on savings and debt reduction is pivotal in fostering financial security and independence, enabling you to navigate life’s uncertainties with confidence and ease.
30% Allocation to Wants
The remaining 30% of your income is designated for wants—those discretionary expenditures that contribute to your lifestyle and personal enjoyment. This category includes leisure activities such as dining out, entertainment, vacations, hobbies, and other non-essential purchases. While these expenses add richness to life, it is imperative to manage them judiciously to prevent financial overreach that could compromise your budgetary balance and long-term financial objectives.
Integrating the 50/30/20 Rule into Your Personal Buget Plan
Incorporating the 50/30/20 rule into your financial strategy can help you navigate the complexities of personal budgeting with clarity and purpose. Here is a calculator to work out your 50/30/20 personal budget: https://www.forbes.com/advisor/banking/budget-calculator/
By delineating clear boundaries for your spending, saving, and debt repayment, this budgeting model empowers you to take control of your finances, ensuring that every rand is allocated efficiently.
To implement this plan effectively, begin by calculating your take-home pay, then apply the 50/30/20 percentages to determine your spending limits in each category. Regularly reviewing and adjusting your budget in response to changes in your financial situation is essential to maintain its relevance and effectiveness.
Adopting the 50/30/20 rule can significantly enhance your financial well-being, providing a structured yet adaptable framework for managing your income.
By conscientiously applying this model, you can ensure that your spending aligns with your immediate needs, your savings goals are actively pursued, and your desires are fulfilled within the boundaries of financial prudence.
The beauty of the 50/20/30 rule lies in its simplicity and flexibility. It offers a straightforward framework for budgeting without the need for detailed tracking of every expense.
This method allows for personal adjustments based on individual circumstances and goals, making it accessible and applicable to a wide range of financial situations.
By adhering to this rule, you can ensure that your essential needs are met, your financial future is secured, and you still have room to enjoy life’s pleasures without compromising your budget.
This balanced approach to budgeting can alleviate financial stress, promote savings, and help you work towards achieving long-term financial stability and freedom.
A personal budget doesn’t have to be complicated. Start with a simple plan that categorizes your spending into needs, wants, and savings. This simplicity can help demystify the budgeting process, making it more approachable and less overwhelming.
Budgeting lays the foundation for robust financial planning. It’s a tool that helps you track your spending, manage your money more efficiently, and make informed decisions about your financial future.
A well-structured budget is a pathway to achieving long-term financial goals, whether it’s buying a house, traveling, or saving for retirement. By allocating funds towards these goals each month, you’re taking steps to make your dreams a reality.
A disciplined budget can significantly ease the process of saving for retirement. By earmarking funds for retirement each month, you’re building a secure financial future without compromising your current lifestyle.
Personal Budgets help prevent overspending, reduce financial stress, and keep you focused on your financial goals. They’re essential for anyone looking to improve their financial health.
A personal budget is more than just a financial tool; it’s a roadmap to financial freedom. It empowers you to live within your means, save for the future, and achieve your financial goals.
Tips for personal budgeting
If you’re someone who finds the meticulous tracking associated with budgeting tedious, there are still effective strategies to manage your finances. Consider the following tips to curb your spending without adhering to a strict budget:
1. Review Your Subscriptions: Regularly assess your ongoing subscriptions, such as insurance, phone services, and entertainment platforms. Reducing or eliminating these can lead to immediate financial relief.
2. Embrace Low-Cost Socializing: Swap expensive dinners and outings for more affordable or free activities. This not only saves money but also encourages creativity in how you socialize.
3. Implement No-Spend Days: Designate certain days as no-spend days to curb impulsive purchases and foster mindfulness in your spending habits.
4. Plan Your Meals: Meal planning and grocery shopping with a list can drastically reduce food costs and minimize the temptation of eating out.
5. Prioritize Saving: Adopt the “pay yourself first” philosophy to ensure that a portion of your income is automatically directed towards savings or debt repayment before covering living expenses.
Conclusion
Incorporating these strategies into your daily routine can lead to significant financial improvements without the need for detailed budget tracking. Remember, the goal of budgeting and financial management is to find a system that works for you, one that supports your financial well-being and helps you achieve your long-term goals.
Monthly budget template ,to draw up a monthly budget or personal monthly budget spreadsheet: https://create.microsoft.com/en-us/templates/budgets


